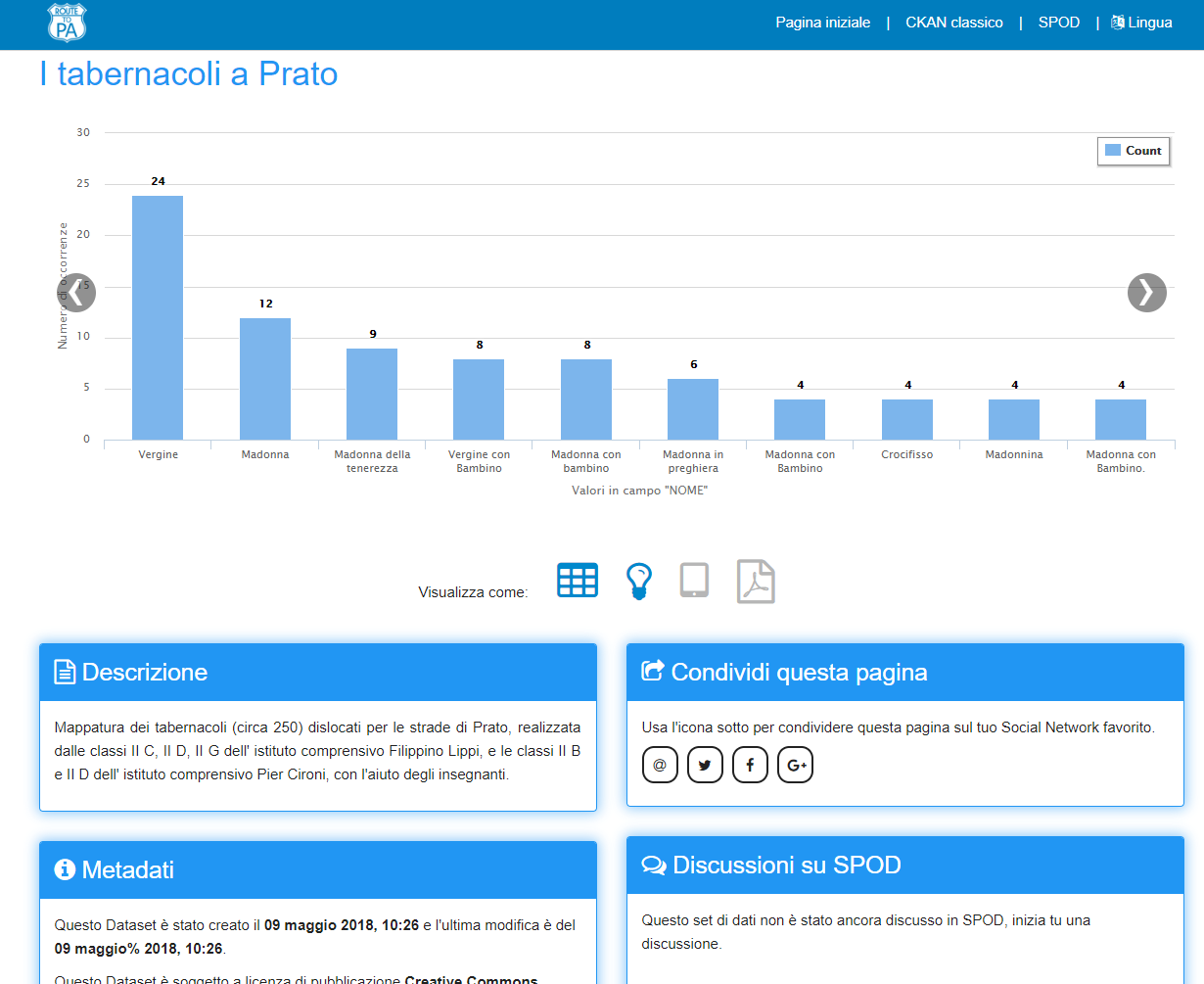
The Transparency Enabling Toolset (TET) comprises a set of tools designed to extend the functionalities of popular open data platforms and in particular CKAN (Comprehensive Knowledge Archive Network) with data accessibility and understandability features. While TET tools can be configured to work with different open data platforms, they are primarily targeted at the CKAN platform.
CKAN is a free open source web-based open data platform and the defacto standard for implementing open data portals. CKAN provides comprehensive data management and data discovery services as well as indexing and full text search. CKAN is designed to facilitate easy discovery of data and has a broad user base. Governments around the world including US, UK, Ireland and Australia, use the platform for making open data accessible to citizens, businesess and other stakeholders. CKAN provides many essential features required to publish, share and visualize datasets and offers powerful cataloging, searching and storing capabilities . CKAN project is implemented and managed by Open Knowledge Foundation (OKF) with many contributions from open source community.
The main objectives of CKAN can be summarized by:
- Freedom of access, creation and dissemination of knowledge.
- Develop, support and promote projects, communities and tools that foster and facilitate the creation, access to and dissemination of knowledge.
- To campaign against restrictions both legal and non-legal on the creation, access to and dissemination of knowledge.
- Act as an intermediary between funding institutions, the creation and diffusion of knowledge projects.
TET is distributed in three modes: 1) as a single all-in-one extension for CKAN, 2) a standalone client application to CKAN and as 3) a set of extensions or plugins for CKAN. Its general architecture is presented in the Figure below.
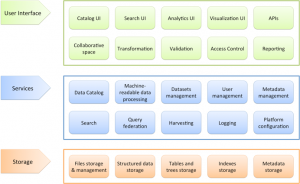
As shown in Figure, the TET architecture consists of three architectural Layers:
(i) User Interface,
(ii) Services,
(iii) Storage layer.
Each of these layers are briefly described below.
User Interface layer
The User Interface layer provides basic portal functions such as access to the data, search interface, personalization and customization features, etc. The search feature allows users to find quickly information stored at the storage layer, while analysis and visualizations features allow users to explore, analyse and visualize various types of data, such as tabular and geospatial data. Various APIs allows external applications to consume services offered by the platform.
Services layer
The Services layer provides services on top of Storage layer that can be exploited by the User Interface layer. Data Catalog services are used to list the details of datasets and associated metadata stored in the platform. Search service uses the index to search relevant content. Platform extensions services allow external applications to use the platform services. All these services have the corresponding features in the interface layer.
Storage layer
The Storage layer is concerned with persistence of data and information and provides all the tools for data storing and efficient retrieving of Open Data. This layer is responsible for storing the files, structured data, tables and trees as well as the indexes and the metadata. Data can be stored directly in file system storage or in the structured data store.